We all are in that phase of time when almost every business activity, customer interaction, and transaction takes place online. Simultaneously, where there’s innovation, there’s exploitation. For example, hackers look for new ways to infiltrate web apps and steal data to disrupt business continuity. This is what makes web application penetration testing more important than ever.
According to Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 by the World Economic Forum…
- 72% of organizations report a hike in their cyber risks in 2024:
- 42% report an increase in phishing and social engineering attacks:
- Ransomware remains one of the key security concerns of organizations:
This 2026 comprehensive guide will review what web application penetration testing is, how the process differs from a basic scan for vulnerabilities, and step-by-step methodologies of testing. Let’s get into it!
What Is Web Application Penetration Testing?
Web app penetration testing is a simulated cyberattack designed to identify security weaknesses in a web application. The goal is to exploit potential vulnerabilities just like a real-world hacker would. These vulnerabilities include broken authentication, SQL injection, or insecure APIs. Lastly, you need to report those flaws to the organization for remediation.
Unlike normal testing, which focuses on functionality, penetration testing focuses on security. This is how you ensure that web app data, users, and back-end infrastructure are not left vulnerable to malicious access. It is usually part of a more general solution for managing vulnerabilities, through which an organization is able to monitor, detect, and take timely action on emerging threats.
Why Web Application Penetration Testing Matters in 2026?
By 2026, 80% of enterprises will be using generative AI APIs or applications. Where there is innovation, however, there’s also a risk. That is why cybersecurity solutions are embracing continuous vulnerability management over one-time assessments. Here, web app pen testing ensures that new updates, integrations, and code changes don’t create security gaps.
Web Application Penetration Testing vs. Vulnerability Scanning
| Aspect | Vulnerability Scanning | Web Application Penetration Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects known vulnerabilities automatically | Simulates real-world attacks to exploit & validate vulnerabilities |
| Method | Automated scan using predefined tools | Manual + automated testing by ethical hackers |
| Depth | Surface-level identification | Deep, contextual exploitation & verification |
| Accuracy | May include false positives | Provides verified, actionable findings |
| Outcome | List of potential issues | Detailed report with proof of exploitation & remediation roadmap |
How to Perform Web Application Penetration Testing Step by Step?
Now that you understand what web application penetration testing is and how it works, it is time to conduct the actual web app penetration testing. Here is a proven structured approach followed by professional security testers and ethical hackers.
Step 1: Planning and Reconnaissance
The QA testers first need to identify the scope, objectives, and the rules of engagement. Tools such as Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and Nmap will help gather key details, such as domain names, IPs, frameworks, backend technologies, etc. Here, the penetration testing team needs to identify:
- Which applications or URLs to test?:
- What kind of attacks are allowed?:
- What are legal and compliance limitations?:
Step 2: Scanning and Enumeration
Having objectives in mind, next you need to conduct web application vulnerability assessments to identify the issues. This creates a foundational view of possible entry points. Rely on automated tools to scan for:
- Misconfigurations:
- Unpatched software:
- Outdated libraries:
- Open ports and exposed APIs:
Step 3: Exploitation and Attack Simulation
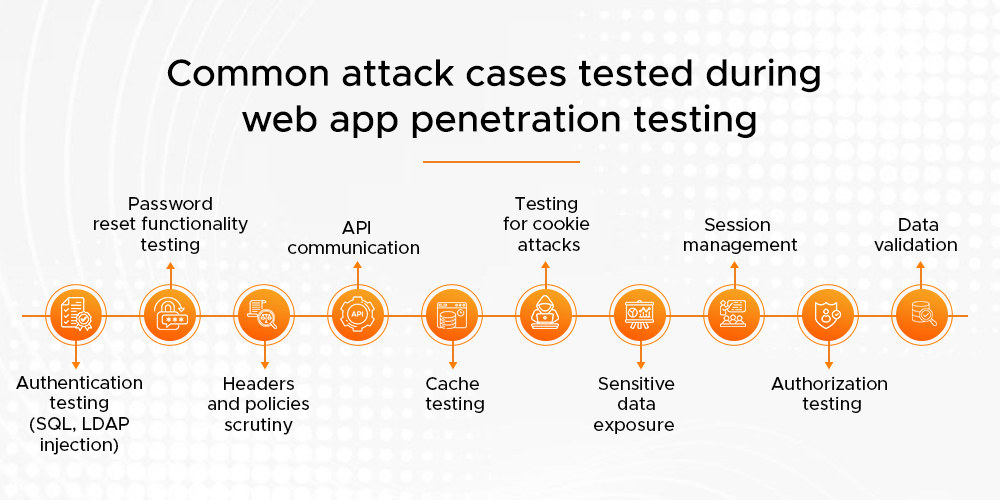
Now comes the real action: attempting to exploit vulnerabilities to determine what an attacker could achieve. Such tests include the simulation of a set of attacks in controlled environments to avoid production disruption. Following is a list of some web application pen testing test cases:
- SQL Injection (SQLi):
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
- Broken Authentication:
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF):
- Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR):
Step 4: Post-Exploitation and Privilege Escalation
Following the exploitation of a vulnerability, testers look at what kind of depth they can achieve when it comes to admin access, exfiltration, or pivoting to other systems. This helps in measuring the impact an attack may have. Quick checklist for a tester post-exploit:
- Capture current user and privilege context:
- Enumerate reachable services and stored credentials:
- Validate the potential for privilege escalation:
- Map lateral movement pathways and potential cross-system impacts:
- Create safe PoC and detailed remediation guidance:
- Clean up artifacts and document chains of custody for all evidence:
Step 5: Reporting and Remediation
It is at this point that vulnerability management solutions step in, with a focus on tracking, prioritization, and effective remediation. You will prepare a detailed report on the following:
- Vulnerabilities found:
- Methods used for exploitation:
- Risk severity levels:
- Recommended changes:
Step 6: Re-testing and Continuous Monitoring
Testing after the application of patches assures one that the identified vulnerabilities have actually been fixed. Then, continuous testing and monitoring are implemented to maintain resilience against evolving threats.
This stage closes the loop on the penetration testing lifecycle and feeds continuous vulnerability management programs with verified outcomes and operational telemetry. Finally, you ensure that vulnerability fixes are real, durable, and measurable.
Ready to Leverage Web Application Penetration Testing in 2026?
At SecureSmartz, we go beyond traditional approaches with strong, flexible artificial intelligence-powered penetration testing. Our solutions range from black box and gray box testing to white box testing to fit your unique needs.
- 25+ Years of Expertise: We have deep domain experience across industries, delivering scalable vulnerability management solutions for multi-cloud setups.
- Certified Testers: Our testing team of seasoned security professionals possesses certifications like CISA, CEH, and OSCP.
- Continuous Testing: From point-in-time assessments to continuous monitoring of your security, we have options that best suit your needs.
- Tailored Approach: We tailor our testing methodologies to align with your web app’s unique architecture and regulatory compliances.
- Actionable Insights: Our detailed reports provide clear remediation guidance for effective mitigation of cyber risks.
In 2026, penetration testing isn’t just about finding flaws—it’s about building digital resilience. By combining penetration testing and vulnerability management solutions with cloud vulnerability assessments, organizations can stay ahead of cyber threats. So, whether you’re launching a new SaaS platform or running an enterprise web portal, we are here to help you make web app penetration testing a core part of your 2026 security strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
SQL injection
XSS
And broken authentication.
